ISCHEMIC STROKE CAUSED BY A BLOOD CLOT
WHAT IS ischemic stroke?
An Ischemic Stroke appears, when an artery carrying blood to the brain is blocked by a clot, or by narrowed arteries.
The blockage reduces or stops the blood flow and therefore causes an undersupply of blood and oxygen to important parts of the brain.
symptoms of STROKE | Notice the signs
Time is brain - ACT F - A - S - TCOMMON RISK FACTORS OF ISCHEMIC STROKE
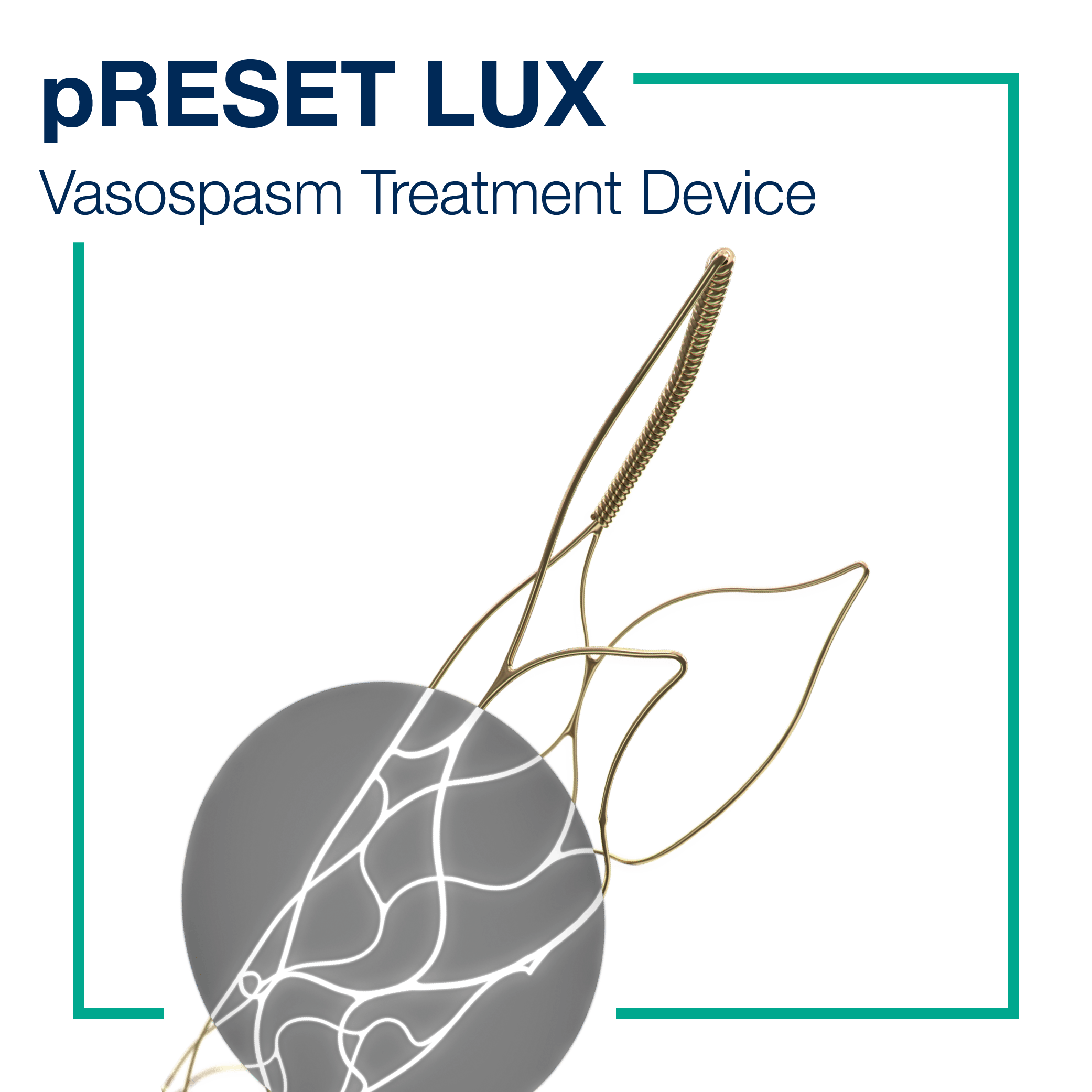
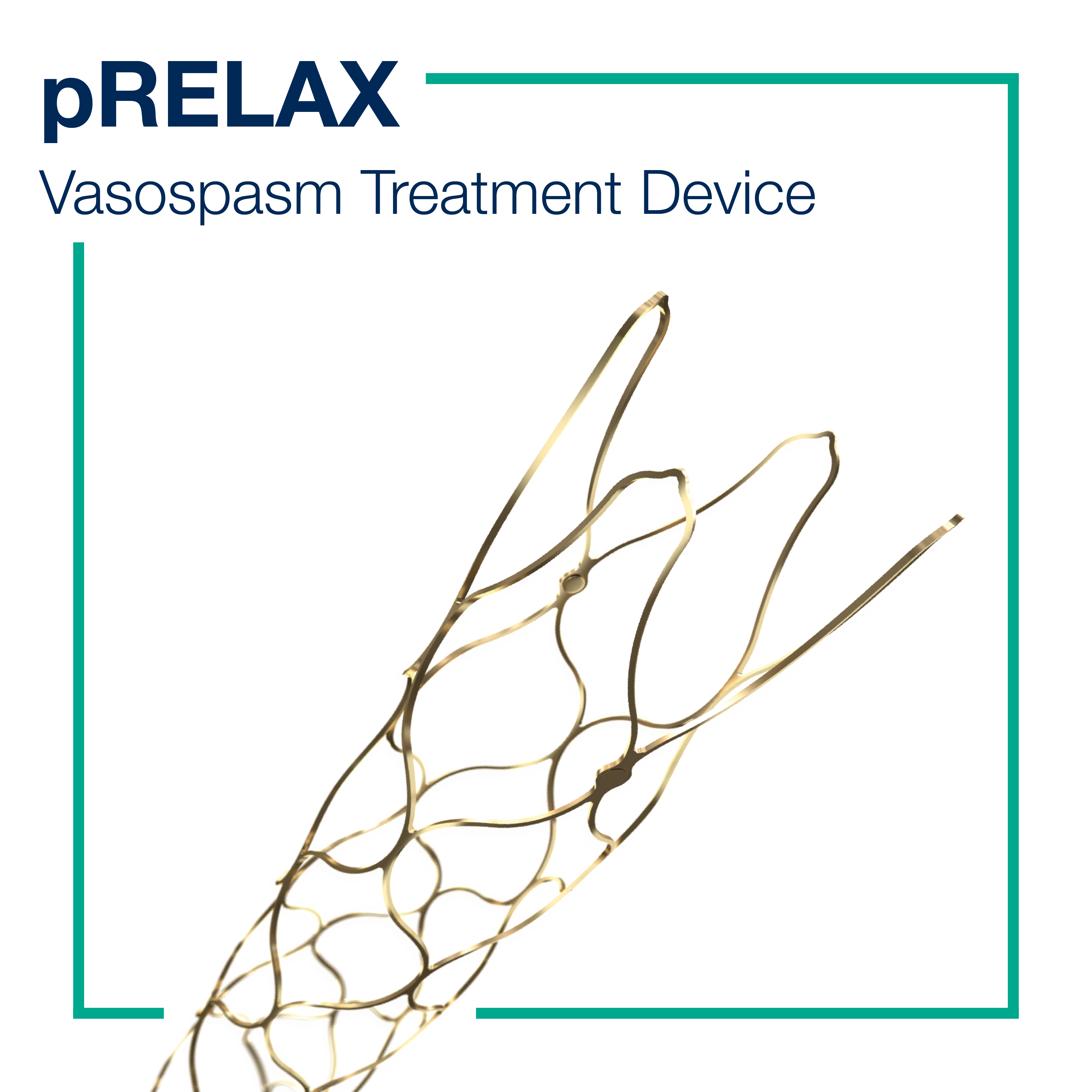
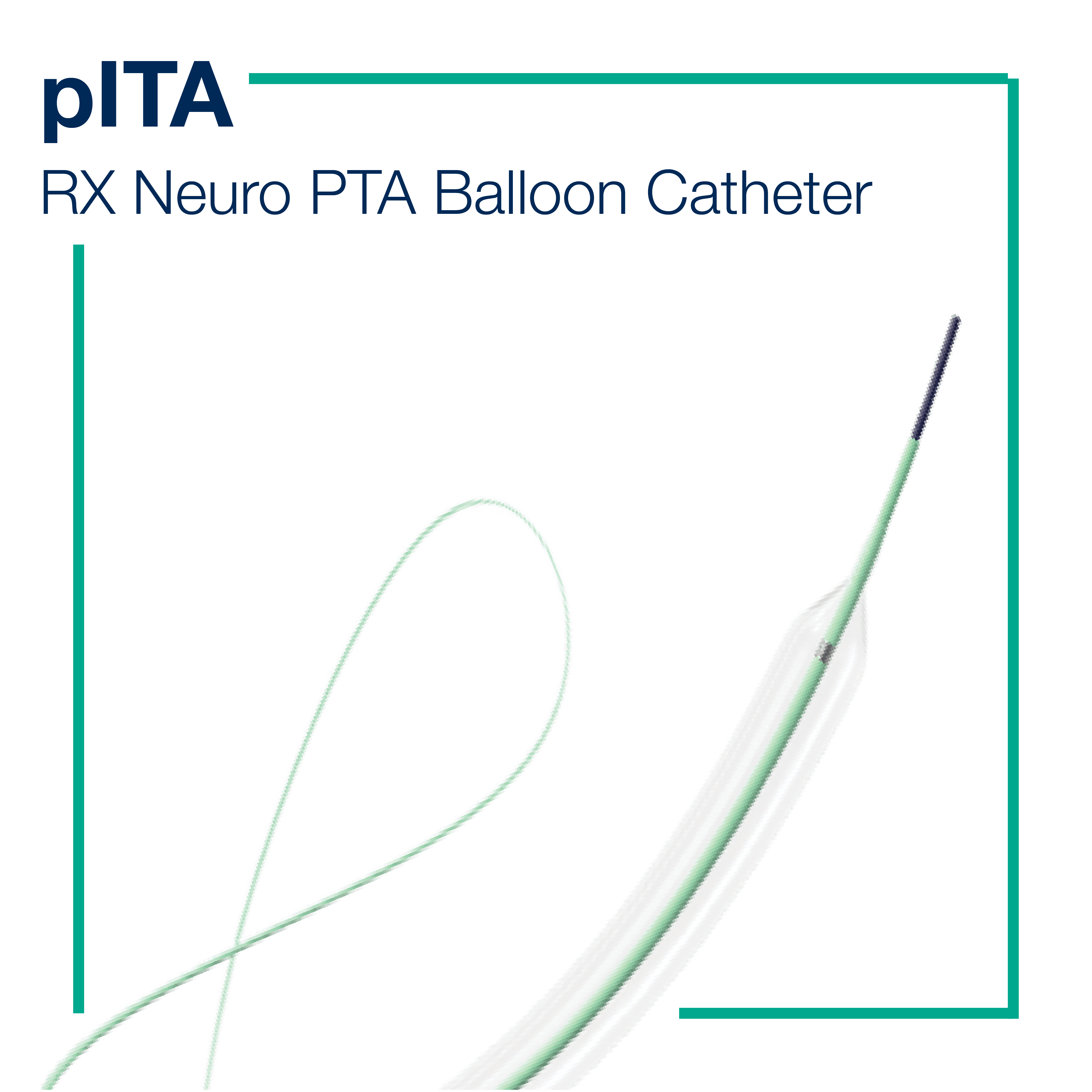
OUR SOLUTIONS FOR ISCHEMIC STROKE TREATMENT
click on the product below to watch them in actionWhich ischemic stroke treatment options are available?
The aim of the treatment is to remove the blood clot from the artery. This can be either done by medical treatment (i.v. lysis) and/or endovascular approach (Mechanical thrombectomy). Treatment options are varying from each case. Factors such as: location, size, and condition play a major role for the chosen treatment.
The endovascular approach is a treatment from within the vessel. It is a minimally invasive procedure which typically only requires a puncture of the groin. Small catheters are navigated through the artery towards the blockage. Treatment devices can be delivered through these catheters.
Mechanical Thrombectomy

Stent Retriever
Stent Retriever is a stent-like device which is delivered through a catheter through the occlusion.
This treatment can be performed using a pRESET Thrombectomy Device. The stent retriever traps the clot inside the device, which is then pulled back into the catheters. Shortly after the removal the blood flow is restored, and the brain is provided with oxygen again.
Which ischemic stroke treatment options are available?
The aim of the treatment is to remove the blood clot from the artery. This can be either done by medical treatment (i.v. lysis) and/or endovascular approach (Mechanical thrombectomy). Treatment options are varying from each case. Factors such as: location, size, and condition play a major role for the chosen treatment.
The endovascular approach is a treatment from within the vessel. It is a minimally invasive procedure which typically only requires a puncture of the groin. Small catheters are navigated through the artery towards the blockage. Treatment devices can be delivered through these catheters.
Mechanical Thrombectomy
Mechanical thrombectomy is an endovascular treatment of an acute ischemic stroke caused by a large vessel occlusion. In order to restore blood flow, a stent retriever and/or aspiration catheter can be used to remove the clot from the brain artery.

Stent Retriver
Stent Retriever is a stent-like device which is delivered through a catheter through the occlusion.
This treatment can be performed using a pRESET Thrombectomy Device. The stent retriever traps the clot inside the device, which is then pulled back into the catheters. Shortly after the removal the blood flow is restored, and the brain is provided with oxygen again.
Which treatment is suitable for my condition?
The aim of the treatment is to remove the blood clot from the artery. This can be either done by medical treatment (i.v. lysis) and/or endovascular approach (Mechanical thrombectomy). Treatment options are varying from each case. Factors such as: location, size, and condition play a major role for the chosen treatment.
The endovascular approach is a treatment from within the vessel. It is a minimally invasive procedure which typically only requires a puncture of the groin. Small catheters are navigated through the artery towards the blockage. Treatment devices can be delivered through these catheters.
Mechanical Thrombectomy
Mechanical thrombectomy is an endovascular treatment of an acute ischemic stroke caused by a large vessel occlusion. In order to restore blood flow, a stent retriever and/or aspiration catheter can be used to remove the clot from the brain artery.

Stent Retriever
Stent Retriever is a stent-like device which is delivered through a catheter through the occlusion.
This treatment can be performed using a pRESET Thrombectomy Device. The stent retriever traps the clot inside the device, which is then pulled back into the catheters. Shortly after the removal the blood flow is restored, and the brain is provided with oxygen again
Sources:
1. Flow Diversion: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/neurology_neurosurgery/centers_clinics/aneurysm/treatment/flow-diversion.html
2. Cerebral Aneurysm: https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/Patient-Caregiver-Education/Fact-Sheets/Cerebral-Aneurysms-Fact-Sheet
3. p64 Flow Modulation Device: https://ec.europa.eu/regional_policy/en/projects/germany/a-better-implant-for-treating-cerebral-aneurysms
4. Causes and Symptoms: https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?ContentTypeID=85&ContentID=P08772
5. Aneurysm Treatment and Diagnosis: https://www.healthline.com/health/aneurysm-in-the-brain#causes
6. Brain Aneurysm: https://www.ohsu.edu/brain-institute/brain-aneurysm
Sources:
1. Flow Diversion: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/neurology_neurosurgery/centers_clinics/aneurysm/treatment/flow-diversion.html
2. Cerebral Aneurysm: https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/Patient-Caregiver-Education/Fact-Sheets/Cerebral-Aneurysms-Fact-Sheet
3. p64 Flow Modulation Device: https://ec.europa.eu/regional_policy/en/projects/germany/a-better-implant-for-treating-cerebral-aneurysms
4. Causes and Symptoms: https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?ContentTypeID=85&ContentID=P08772
5. Aneurysm Treatment and Diagnosis: https://www.healthline.com/health/aneurysm-in-the-brain#causes
6. Brain Aneurysm: https://www.ohsu.edu/brain-institute/brain-aneurysm